Synonyms:
Gentiana, Gentian Root, Gentiana Radix
Botanical source:
Gentian consists of the dried roots and rhizomes of Gentiana lutea Linn., a herbaceous perennial plant of the family Gentianaceae.
Gentian Root Geographical source:
The plant is indigenous to Central Europe and the drug is exported from Spain.
Macroscopical characters:
The drug occurs in nearly cylindrical pieces, often 5O cm or longer and up to 2.5 cm thick. It is sometimes longitudinally split. There are longitudinal wrinkles on the cork of the root, while the rhizome is encircled by crowded leaf scars. It is yellowish brown in colour and breaks with a short fracture showing a starchy surface. The transversely cut surface is almost uniformly reddish yellow in colour with a distinct cambium and a radiate wood. A pith is present in the rhizome. The drug has a characteristic odour and a characteristic taste, which is sweet at first and then persistently bitter.
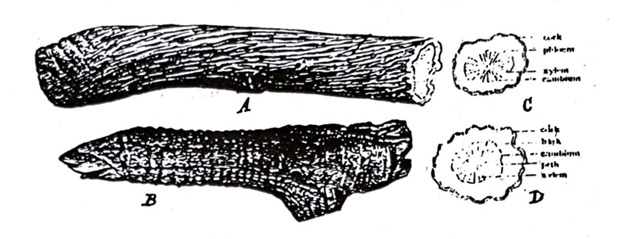
Fig. 56: Gentian. A root.; R, rhizome; C, transverse surface of root; D, transverse surface of rhizome. (Reconstructed from Wallis and Hebert & Ellery).
Microscopical characters:
The cork consists of several layers of thin-walled tangentially elongated cells containing oil globules. Cortex is narrow and is made up of tangentially elongated collenchymatous cells containing a brownish granular substance, oil globules, and minute needle-shaped calcium oxalate crystals. The outer phloem tissue consists of large cells with intercellular spaces and prominent nuclei. All phloem cells contain oil globules and minute needles of calcium oxalate. Xylem tissue consists principally of parenchymatous cells traversed by medullary rays. They also contain oil globules and minutes needles of calcium oxalate. The vessels occur scattered, either isolated or in small groups, in the parenchymatous tissue.
Chemical constituents:
Gentian contains a large number of bitter glycosides, which include gentiopicrin, gentiamarin, gentiin, etc. It also contains free sugars, gentianose and sucrose, enzymes, a yellow coloring matter, pectin, and an oil.
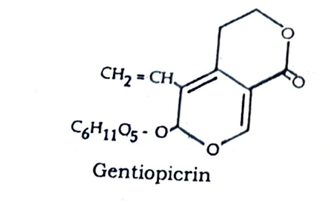
Uses of Gentian Root:
Gentian is used as a very favorite bitter tonic.
Substitutes and adulterants:
The dried roots and rhizomes of the following plants are frequently used as substitutes and adulterants of Gentain: Gentiana purpurea, G. pannaonica, G. punctata, Rumex alpinus (Polygonaceae) and Veretrum album (Veretraceae)
