Synonyms of Aconite Root:
Aconitum, Aconite Root, Radix Aconiti.
Botanical source:
Aconite consists of the dried tuberous roots of Aconitum napellus Linn., a perennial herb of the family Ranunculaceae.
Geographical source:
Aconite is obtained from plants cultivated in England and from wild plants growing in the mountain slopes of Germany, Switzerland and France.
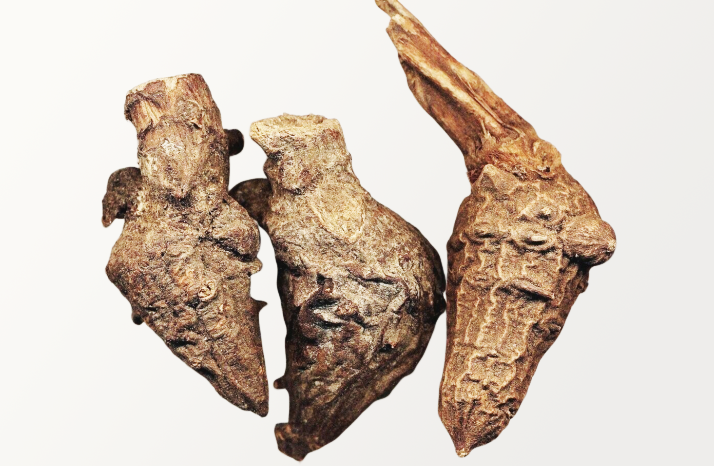

Aconite Root Macroscopical Characters:
The root is obconical in shape, 4 to 10 cm long and 1 to 3 cm wide at the crown. The surface exhibits longitudinal ridges and numerous rootlets. One or more daughter roots occur: attached to the parent root. An apical bud is present at the top of the daughter root, and the base of an aerial stem is attached tot he crown of the parent root. It is brown to dark brown in colour. The whole root has a short fracture, breaks with a starchy fractured surface. The transversely cut surface of root shows a stellate cambium. It has a slight taste with a tingling and numbing sensation.
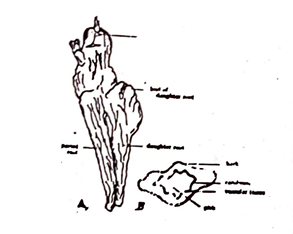
Fig. 54: Aconite. A, whole drug; B, transverse surface. (After Hebert & Ellery)
Microscopical Characters:
The outer ground tissue consists of subcrised parenchymatous cells. The cortex is about 20 cells wide, bounded inside by an endodermis with suberised cell walls. Some characteristic sclereids occur in the cortex. Xylem tissues of the radial vascular bundles are composed of small groups of pitted and reticulate vessels embedded in parenchyma. The pith is large and composed entirely of parenchymatous tissue containing starch grains.
Chemical constituents:
Aconite principally contains three closely related alkaloids, namely, aconitine, picraconitine and aconine. It also contains small amounts of other alkaloids, aconitic acid and starch.
Uses of Aconite Root:
Tinctures of Aconite and aconitine are used externally in certain forms of neuralgia and rheumatism, and internally m small doses in cases of fever and pain.
Substitutes and Adulterants:
The common substitutes and adulterants of Aconite include the dried roots of Aconitum uncinatum var. japonicr1m (Japanese Aconite), Aconitum deinorhizum (Indian Aconite), Aconitum tianshanicum (Russian Aconite), Aconitum heterophyllum (A tis Root) and Aconitum chasmanthum.
