Synonyms:
Ordeal Bean, Esere’ Nut, Physostigmatis Semina.
Botanical Source:
Calabar beans are the ripe seeds of the legumes of Physostigma venenosum Balfour, a perennial woody climbing plant of the family Papilionaceae.
Geographical Source of Calabar Beans:
The plant is indigenous to the West Coast of Africa and grows on the banks of streams in West Africa.
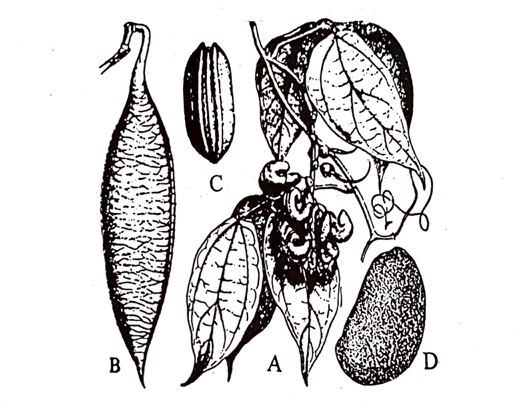
Fig. 44: Physostigma venenosum: A, flowering branch; B, a fruit; C, a seed (hilum side); D, seed (side view). (Reconstructed from Claus & Tyler).
Macroscopical and Microscopical Characters:
The legumes of Calabar beans are about 15 cm long and contain two or three large seeds, which are 25 to 30 mm long. 15 to 18 mm broad and 10 to 15 mm thick and are oblong reniform in shape. The seed coat is hard, thick and shiny. It is dark reddish brown in colour. The hilum extends throughout the length of curved edge of the seed and round its more blunt end forming a deep black grove, about 2 mm wide. The micropyle is situated at the acute end of the seed adjacent to the end of the hilum. There are cotyledons inside the testa, which are concavo-convex in shape and enclose sufficient air to enable the seed to float in water. They possess no characteristic odour or taste, but are·highly poisonous.
Calabar Beans Chemical Constituents:
The chief constituent of Calabar bean is The chief constituent of Calabar bean is the physostigmine (eserine) (0.04 to 0.3 %), which is the medicinally useful alkaloid. It also contains starch (about 48 %) and proteins (23 %). In addition, the Calabar bean contains small quantities of a number of other alkaloids, which include geneserine, eseramine, iso-physostigmine, physovenine, nor-physostigmine, calabatine and calabacine, and a small amount of fixed oil. 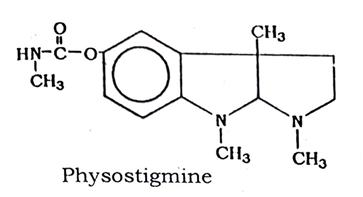
Uses of Calabar Beans:
Physostigmine extracted from the Calabar beans is used to produce contraction of the pupil of the eye. It has been employed in the treatment of tetanus and as an antidote for strychnine poisoning. Large dose of the alkaloid causes death by increasing blood pressure and suffocation.
Substitutes and Adulterants:
Seeds of Physostigma cylindrospermum. Mucuna urens, Entada scandens, and Pentaclethra macrophylla have been used to substitute and adulterate Calabar beans.


🪴🫶thank you this was helpful
Can it be cultivated?