Synonyms of Capsicum
Capsicum Fruits, Chilies, Capsici Fructus
Botanical source
Capsicum consists of the dried ripe fruits of Capsicum minimum Roxb. and also of Capsicum frutescens Linn., which are perennial shrubs of the family Solanaceae.
Geographical source
Capsicums are widely grown and cultivated throughout East and West Africa, India Sri Lanka, Bangladesh, Japan, and South America.

Macroscopical characters
Capsicum fruits are bilocular berries, oblong-conical to ovoid-conical or ovoid in shape, 12 to 20 mm long and 4 to 7 mm broad. The pericarp is glabrous, somewhat shrunken, leathery and thin, more or less translucent and dull orange-red in colour. The fruit contains five to ten seeds in each loculus. The seeds are· disc-shaped, slightly pointed at one end, orange-yellow in colour, about 3 to 4 mm long, 2 to 3 mm broad and 0.5 to 1.0 mm thick. The hilum and micropyle are situated at the pointed end. A narrow, coiled embryo is embedded in the oily endosperm. The fruit often exhibits an inferior, greenish brown, 5-toothed persisting calyx and a 5 to 10 mm long, thin, straight or curved pedicel. Capsicum fruit has a characteristic odour and a strong pungent taste. Some cultivated varieties are however non-pungent.
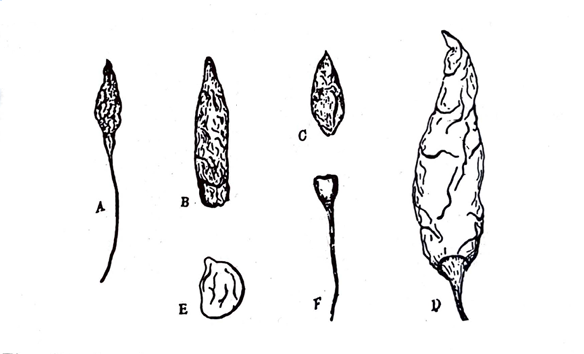
Fig. 39: Capsicum. A, Zanzibar; 8, Japanese; C, Sierra-Leone, D, Bombay; E, seed; F, calyx and pedicel. (Reconstructed from Hebert & Ellery).
Capsicum Microscopical characters
The pericarp is divisible into four distinct regions:
- The outer epidermis, which is composed of cuticularised five to seven rows of rectangular cells;
- The parenchymatous ground tissue of the mesocarp, which is made up to rounded tissue of the mesocarp, which is made up . to rounded cells with cellulose· walls, most of them containing yellowish oily droplets and yellowish-red chromatophores, some of them also contain sandy crystals of calcium oxalate.
- A single layer of very large cells with cellulosic walls
- The endocarp, which consists of moderately thick-walled, pitted and lignified cells with wavy walls.
They form a number of islands in the endocarp beneath most of the cells of the large-celled layer. The seed epidermis con·sists of cells with wavy anticlinal walls and heavy lignified thickening of the horseshoe or beaker-shaped type. The polyhedral cells of the endosperm contain fixed oil and aleurone grains.
Chemical constituents
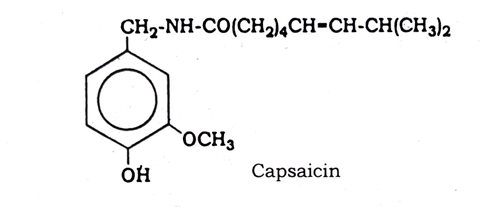
Capsicum contains 0.05 to 0.14 percent of a pungent principle, known as capsaicin. It also contains 1.5 percent of volatile oil, 0.2 percent of ascorbic acid, a small quantity of a volatile liquid alkaloid, a fixed oil, carotene, and a red coloring matter, capsanthin.
Uses of Capsicum
Capsicum is a stimulant and counter-irritant. It is used externally in the form of ointment and plaster. It is internally used as a pungent stomachic carminative and stimulant in the treatment of flatulence and dyspepsia.
Substitutes and adulterants
There are large varieties of capsicum and chilies grown all over the world which are used as adulterants and substitutes for Capsicum minimum. These include Japanese chilies, Bombay capsicum, Natal capsicums, and Bird Pepper.

