Synonyms:
Castor oil Seed, Ricini Semina, Castor
Botanical Source:
Castor seeds are obtained from the ripe fruits of Ricinus communis Linn., a shrub or small tree of the family Euphorbiaceae.
Geographical Source of Castor Seeds:
The plant is a native of India, but now commonly grows wild in almost all tropical countries, notably South America, Bangladesh, Nigeria and other countries of tropical Africa.

Macroscopical and Microscopical Characters:
The plant varies greatly in size and nature when it grows in different geographical areas. This variation is also apparent in the size of the seeds. Seeds are about 8 to 18 mm long, 4 to 12 mm broad and 4 to 8 mm thick; slightly flattened and oval in shape, the flatter ventral surface being slightly ridged. A small yellowish caruncle is usually present at one end, from which runs a distinct raphe to terminate in a slightly raised chalaza at the opposite end of the seed. The testa is hard, glossy and smooth, grayish to reddish brown, With reddish-brown or black variously mottled spots and stripes. Within the testa is a soft white thin papery membrane which forms a cover around the large oily endosperm.
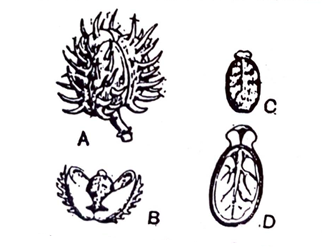
The endosperm has a long but very narrow central cavity in which lie the two colorless leafy cotyledons of the embryo. The seeds possess little odour and an acrid taste.
Chemical constituents:
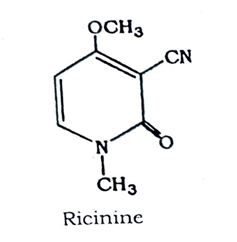
Castor seeds contain about 50 percent of fixed oil and 26 percent of protein. It also contains a crystalline principle, ricinine (0.2%), a toxin, ricin and ‘an enzyme, lipase.
Uses of Castor Seeds:
Extracts of Castor seed and Castor oil are used as h3 purgative drugs.
Allied drugs:
These include Croton seeds, obtained from Croton tiglium and Purging Nuts, which are seeds of Jatropha curcas.

