Corms are condensed forms of rhizomes consisting of stout, solid, fleshy underground stems growing vertically. They are usually more or less rounded in shape or often somewhat flattened. Corms bear one or more buds in the axils of scale leaves. They produce adventitious roots on their under surface and also on their sides. Colchicum corm is a good example of corm drugs.
COLCHICUM
Synonyms:
Colchicum Corm, Colchicum Root, Colchici Cormus, Colchici Radix.
Botanical source:
Colchicum consists of the fresh or dried corm of Colchicum autumnale Linn. (Family Liliaceae), deprived of its coats.
Geographical source:
The plant grows throughout Europe, particularly in England, Holland and Italy.
Macroscopical characters:
The fresh whole corm is ovoid or sub-conical in shape, about 4 cm long and 3 cm broad. The dried slices are reniform, vary in width from 2 to 3 cm and the average thickness is 4 mm. The corm is crowned with bases of flowering stem at the apex, a small bud -near the base on the flattened side and fibrous roots at the base. The dried slice exhibits a thin, brown, membranous epidermis and numerous fibrovascular bundles as brown spots against a white ground tissue. It has a short fracture with a mealy fractured surface. The drug has got no odour, but possesses a very bitter and acrid taste.
Microscopical characters:
The epidermal cells are rectangular to polygonal in shape and have brown, thick and slightly wavy walls.
The epidermis contains occasional circular stomata. The major bulk of the corm is made up of thin-walled rounded parenchymatous cells filled with abundant simple or compound starch grains. Muller shaped starch grains often occur. Vascular bundles are slender and collateral and run longitudinally through the corm. Xylem vessels are narrow with spiral or annular thickening
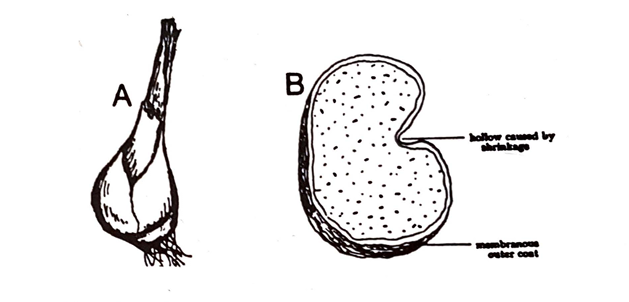 Fig. 69: Colchicum. A, fresh whole corm; B, transversely cut slice of dried corm. (Reconstructed from Hebert & Ellery).
Fig. 69: Colchicum. A, fresh whole corm; B, transversely cut slice of dried corm. (Reconstructed from Hebert & Ellery).
Chemical constituents:
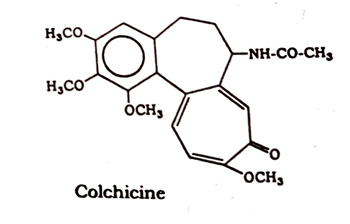
The drug contains an almost NH-CO-CH, neutral toxic alkaloid, called 0 colchicine (about 0.5 -0.6 percent), and abundant starch grains.
Uses:
Colchicum corm is used mainly to treat acute attack of gout and certain other gouty affections. It relieves the pain and inflammation caused by gouty affections, and shortens the duration of these diseases. The alkaloid, colchicine, induces polyploidy in plants by arresting spindle formation during mitotic cell division. This property of colchicine is used in agricultural research to produce larger varieties of agricultural products and to induce higher yields of crops and vegetables.
Bulbs consist of a shortened convex or slightly conical stem, a terminal bud and numerous scale leaves. The scale leaves grow from the upper surface of the stem or from around it, while a cluster of adventitious roots arise from its base. Drugs, which are represented by the fleshy scale leaves of bulbs, include Squill, Garlic and Onion.


So informative for exam point of view