Extracts, which constitute unorganised drugs, are usually prepared by evaporating the aqueous decoctions of various parts of certain plants. Two representative examples of such drugs J prepared from dried plant extracts are briefly described below in the form of Monographs.
CATECHU
Synonyms:
Gambier, Pale Catechu, Terra Japonica
Biological source:
Catechu is a dried aqueous extract, prepared from the leaves and young shoots of Uncaria gambier (Hunter) Roxb., a climbing shrub of the family Rubiaceae.
Geographical source:
The plant is indigenous to Malaysia and is cultivated in the islands between Singapore and Sumatra.
Macroscopical characters:
Catechu occurs as regular cubes, 2 to 3 cm in each dimension, or in masses of adherent cubes, or in irregularly broken pieces. The surfaces of the cubes are even, with a few minute cavities, dull greyish brown to dark reddish brown in colour. The cubes have a brittle fracture with a pale brown, friable and porous fractured surface. The drug has no odour, but has a distinct taste which is initially bitter and astringent but afterwards sweetish. ·It is soluble in hot water and alcohol.
Microscopical characters:
When examined under the microscope in lactophenol, the drug exhibits numerous acicular crystals of catechin. The residue obtained after dissolving the drug in water or alcohol contains pieces of epidermis, trichomes and other vegetable debris.
Chemical constituents:
Catechu contains 7 to 33 percent of catechin, 22 to 50 percent of catechutannic acid, and small quantities of catechu-red, quercetin and gambier nuorescin.
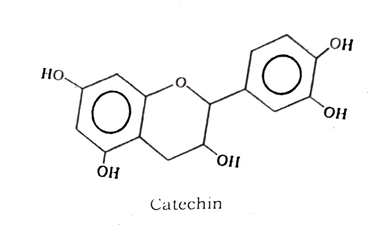
Uses:
Catechu is medicinally used as a local or general astringent drug. It is used in dyeing and tanning industries. It is very commonly eaten in Asian countries along with betel leaf for its soothing effects.

