Juices are natural aqueous fluids that drain out from cut surfaces of plant parts or are obtained by cutting plant parts into pieces, squeezing and straining the fluid out them. An important example of such drugs prepared from dried juices is described below in the form of a Monograph.
ALOE
Synonym:
Aloes
Biological source:
Aloe consists of the evaporated juice, which drains from the cut leaves of various species of Aloe (Family Liliaceae). According to their natural sources, the following three commercial varieties of Aloe are recognised.
1. Cape aloe (obtained from Aloe ferox Mill.)
2. Curacao aloe (obtained from Aloe vera Linn.)
3. Socotrine aloe (obtained from Aloe perryi Baker)
Geographical source:
Aloe plants are indigenously grown in various East African countries and in South Africa. They are cultivated in West Indian Islands.
Macroscopical characters:
Aloe occurs in hard irregular masses of variable size. The surface of Cape aloe is glassy; Curacao aloe, dull and waxy, and Socotrine aloe, dull and irregular. They also differ from each other in colour: Cape alone has a dark brown or greenish-brown colour; Curacao aloe, a reddish-brown colour, and Socotrine aloe, a dark brown colour. Aloe breaks with a brittle fracture. The fractured surfaces and pieces are characteristic of the three
commercial forms: Cape aloe has a glassy fractured surface and its thin pieces are transparent; Curacao aloe has uniform waxy surface and the pieces are opaque, and Socotrine aloe has an uneven porous fractured surface and the pieces are opaque. Cape aloe possesses a characteristic sour odour; Curacao aloe has an unpleasant penetrating · odour, and the Socotrine aloe has a strong, characteristic unpleasant odour. All of them possess a very bitter and nauseous taste. They are soluble in water and 60 percent alcohol.
Microscopical characters:
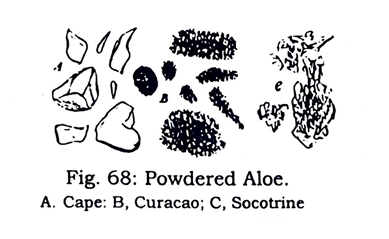
Powdered forms of the three varieties of Aloe can be easily distinguished under the microscope. When mounted in lactophenol, Cape aloe appears as transparent, brown, irregular and angular fragments; Curacao aloe shows fragments composed of innumerable minute slender prisms or needles, and Socotrine aloe shows fragments composed of fairly large prisms, which irregularly group into masses of different sizes (see Fig. 68).
 Chemical constituents:
Chemical constituents:
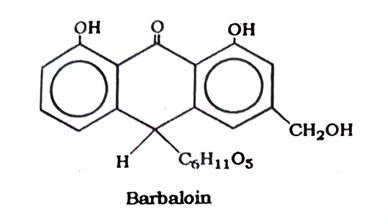
The principal constituents of Aloe are anthraquinone glycosides, the most important of which is barbaloin. The others include iso-barbaloin, Beta-barbaloin and aloe-emodin. Aloe also contains a pale yellow volatile oil and resin.
Uses:
Aloe is used as a cathartic drug. It is a valuable purgative in different forms of constipation, particularly the habitual constipation. Aloe is also used as a pharmaceutic necessity in Compound Benzoin Tincture.
