Synonyms:
Licorice, Liquorice Root, Glycyrrhiza, Glycyrrhizae Radix
Botanical source:
Liquorice is derived from the stolons and roots of Glycyrrhiza glabra Linn. and other species of the genus Glycyrrhiza (Family Papilionaceae).
Geographical source:
Glycyrrhiza glabra is cultivated in England, Sicily and Spain. It is also grown in Turkey, Iraq, Iran, Italy, France and Germany.
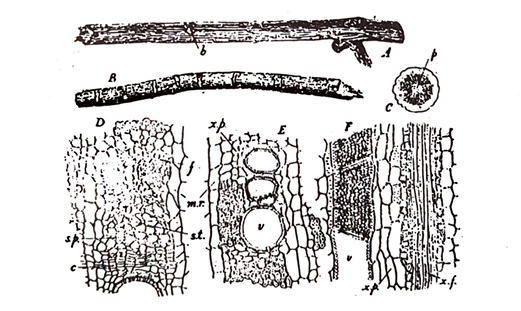
Fig 61: Liquorice. A, a stolon; B, a root; C, t.s. of a stolon; D, t.s of the phloem E, t.s em; of the xylem F, radial ls. of the xylem. b, bud; c, cambium; F phloem fibres, m. r., medullary ray; p, pith; s.p., sieve plate; s.t., sieve tube; v, vessel; x.f., xylem fibres; x.p., xylem parenchyma. (Adopted from Wallis)
Macroscopical characters:
The stolons are cylindrical in shape and occur in pieces of 15 cm or more in length and 1 to 2 cm in breadth. They are unbranched and may be unpeeled or peeled. The unpeeled drug is longitudinally wrinkled with occasional buds and the peeled drug is coarsely fibrous on the surface. The colour varies from yellowish brown to dark brown (unpeeled drug) and pale yellow (peeled dru_. The fracture is fibrous, the fractured surface being starchy with projecting fibres. The transversely cut surface shows a radiate wood and a distinct cambium ring. A pith is visible in the stolon but is absent from the root. It has a faintly characteristic odour and sweet taste.
Microscopical characters:
The peeled drug contains no cork. But the unpeeled drug contains a typical cork, the outer cells of which have thick walls and contain a reddish brown substance and the inner cells have thinner walls. The cortex contains idioblasts with prisms of calcium oxalate. The phloem tissue is made up to parenchyma traversed by numerous groups of sieve tubes and is characterised by the presence of numerous bundles of thick walled fibres surrounded by a sheath of idioblasts with calcium oxalate prisms. The xylem tissue is divided into sections by 3 to 4 cells wide large medullary rays and is composed of numerous yellow pitted vessels, lignified wood parenchyma and wood fibres. Large number of rounded starch grains are present in the parenchymatous cells.
Chemical constituents:
Liquorice contains 5 to 7 percent of glycyrrhizin (a sweet principle made up of potassium and calcium salts of glycyrrhizic acid). It also contains glucose sucrose a bitter principle, starch fat and calcium oxalate.
Uses:
Liquorice is used as a demulcent and expectorant. It is also used in the treatment of gastric and duodenal ulcers.
Substitutes and adulterants:
The Russian and Iranian varieties of Liquorice ( (Glycyrrhiza glabra) var. glandulifera and Glycyrrhiza glabra var. violacea respectively) and Manchurian Liquorice are common substitutes and adulterants of Liquorice.
