Synonyms:
Turmeric Rhizome, Curcumae Rhizoma
Botanical source:
Turmeric consists of the boiled and dried whole or split and unpeeled rhizome of Curcuma domestica Val. and Curcuma longa Linn. of the family Zingiberaceae.
Geographical source:
Turmeric is obtained from plants cultivated in India, China, Indonesia, Bangladesh and Asian countries. It is also cultivated in Nigeria and many other tropical countries.
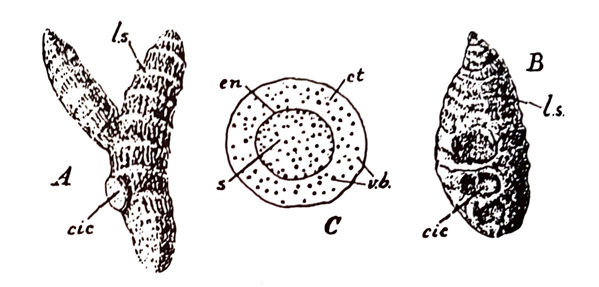 Fig. 65: Turmeric A, finger turmeric; 8, bulb turmeric; C, t.s. of rhizome. cic, circular scar of branch; ct, cortex; en, endodermis; l.s., leaf scar; s, stele; v.b., vascular bundle. (Reproduced from Wallis).
Fig. 65: Turmeric A, finger turmeric; 8, bulb turmeric; C, t.s. of rhizome. cic, circular scar of branch; ct, cortex; en, endodermis; l.s., leaf scar; s, stele; v.b., vascular bundle. (Reproduced from Wallis).
Macroscopical and microscopical characters:
Turmeric occurs in whole forms as fingers and bulbs or in longitudinally split pieces. The fingers and bulbs are cylindrical or sub-cylindrical in shape, bluntly tapering at both ends. The outer surface is deep yellowish brown in colour, longitudinally wrinkled and marked with transverse rings of scars of scale leaves. Short knob like branches and large circular scars of broken off branches often occur on the surface. The drug is hard and heavy and breaks with a short fracture.
Internally the drug is uniformly dull brownish yellow in colour with a waxy appearance. The transversely cut surface shows a paler or darker endodermal ring separating the stele from the cortex, in both of which numerous fibrovascular bundles remain scattered. The ground tissue is made up of parenchymatous cells, which contain masses of gelatinised starch grains. The drug has a characteristic aromatic odour and a somewhat bitterish unpalatable taste.
Chemical constituents:
Turmeric contains about 6 per cent of volatile oil, and about 5 per cent of a crystalline yellow substance, curcumin. It also contains resin, sugars and starch.
Uses:
The fresh juice of Turmeric is used internally as a blood purifier. The paste or cream of the rhizome is applied externally for brightening the colour of the skin. The hot paste of the rhizome is used as a poultice in the treatment of inflammations and joint pains. Turmeric is also used as a colouring and dyeing agent. It is commonly used as a condiment, particularly in the Asian and African countries.

